Horticulture lighting is the method for stimulating plant growth by artificial lighting fixtures, when natural light is lacking.
Horticulture lighting is the method for stimulating plant growth by artificial lighting fixtures, when natural light is lacking.
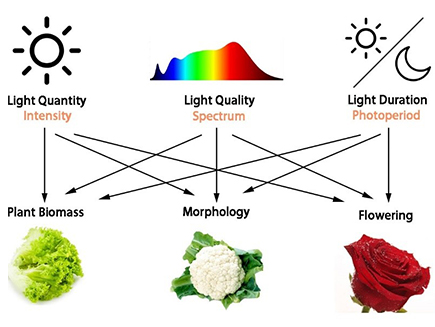
Professional horticulture lighting is not only about providing sufficient light for plant growth through the improvement of photosynthesis, but also about helping plants to produce more beautiful flower, better shape of leaves and more fruit as well as shorten or extend a specific growing period.
For professional horticulture lighting, the proper tailored recipes are essential for optimization of plant growing in purpose. The specific needs of different plants in each growing period and each part of plant organs determine which lighting recipe is better for optimize growth.
KEY POINTS OF HORTICULTURE LIGHTING RECIPES:
Supplement lightingPhotoperiod control
Photo-morphologic controlPlant organs growth needs
Growth
Apart from the factors including temperature, humidity, water, oxygen, carbon and nutrients, special characteristics of lighting also play a significant role to control the plant growth. The light intensity, spectrum and duration impact plants' morphology, growth, fruiting as well as flowering.
Photosynthesis
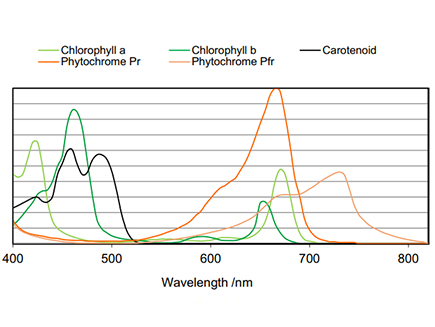
Plants can convert light energy into chemical energy by photosynthesis. Plants need to absorb special light spectra emitting in order to generate necessary element, such as chlorophyll, anthocyanin, carotenoid and phytochromes, within its organs for growing. A professional horticulture lighting recipe should optimize the spectrum of light source to meet plants needs for photosynthesis in order to maximize the growth speed of plants and minimize the electrical energy consumption simultaneously.
What does plant care?
PAR: photosynthetic active radiation
Photosynthetic active radiation, also called as PAR, stands for the spectral range of solar radiation from 400nm to 700nm. It defines the light the plant needs to support photosynthesis. In this range, plants’ photosynthetic organisms are able to absorb light in the process of photosynthesis.
PPF: photosynthetic photon flux
Photosynthetic photon flux (PPF) is a measurement that determines the total amount of photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) a light gives off. It values all photons from 400nm to 700nm based on plant's photosynthetic response.
PPFD: photosynthetic photon flux density
Photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) is another measurement provides same information as PPF. It also stands for the photons in the spectral range of 400nm to 700nm. While the difference of them is that PPF measures how many photons get off from a light source. On the other hand, PPFD is about how many photons drop on a surface area in square meter.
DLI: daily light integral
Daily light integral (DLI) represents the number of PAR that are delivered to a square meter area in a day and night (24 hours). Sometimes, this value also is calculated in second. Generally, 10 and 30 mol·m-2·d−1.